50% Off Blow Out Sale – Fentanyl Test Strip 20ng/ml – Individual Pouch
$1.05 Original price was: $1.05.$0.69Current price is: $0.69.
As Low As $0.29
Cutoff level: Fentanyl 20 ng/ml
Fentanyl Drug Test
Fentanyl Drug Test is an easy way to detect the presence of fentanyl drug in human urine or any other liquid (solution).
Key futures of fentanyl drug test are:
- They are low cost
- 99% accurate
- results are shown after 5 min
- you can test any kind of solution preventing overdosage
- Forensic use only
Fentanyl is known to be a synthetic opioid connected with the family of phenylpiperidines. It is more dangerous than morphine and tends to dissolve in lipid causing damage to the human brain.
How do fentanyl test work
The FYL Rapid Test Strip (Urine) detects fentanyl through visual color change on the strip and then confirm the absence or presence of fentanyl.
The antibody-drug conjugates are deactivated on the test region of the membrane.
During the test, the collected urine specimen reacts with antibodies conjugated to colored particles and percolated on the sample pad.
Procedure of the Fentanyl Test Strip Bring test, specimens, buffer, and/or controls to room temperature (15-30 degree Celsius) before use.
Instructions for Fentanyl urine testing
Bring tests, specimens, buffer and/or controls to room temperature (15-30°C) before use, then just follow few simple steps.
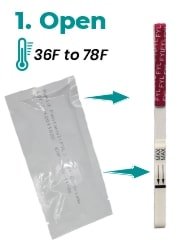
- Open: Remove the fentanyl drug test Stripe from its sealed pouch, or remove one strip from the canister, and use it as soon as possible. For the best result, the assay should be performed within an hour.
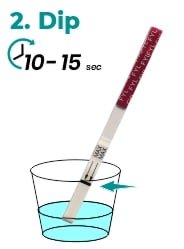
- Dip: Hold the fentanyl drug test by the end, where the product name is printed. To avoid contamination, do not touch the strip membrane. Dip the test strip in the urine specimen for at least 10-15 seconds. Do not immerse past the maximum line (MAX) on the test strip.
- Wait: After the test has finished running, remove the fentanyl drug test from the specimen and place it on a non-absorbent flat surface.
- Read: Start the timer and wait for the colored band(s) to appear. The result should be read at 5 minutes. Do not interpret the result after 10 minutes.

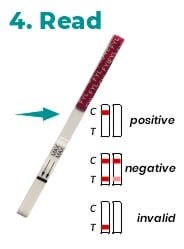

Positive

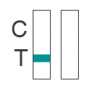
Negative
Invalid
Fentanyl Urine Drug Tests as an overdose protection
If we were to make a scale of the strongest drugs in the market today Fentanyl would undoubtedly rank very high on that list.
This poses a significant danger as the threshold for overdosing on fentanyl is much lower than most drugs.
This is sadly often used today in illegal drug sales, as more and more products such as cocaine are combined with fentanyl powder.
This combination of cocaine and fentanyl in particular is known to be quite lethal, leading to overdose in most cases.
The fact that there is no regulation on how many of the illegal drugs are produced leads to very dangerous compounds which can and will kill the person ingesting them. Fentanyl drug test are a great way to protect yourself.
You can find fentanyl test strips for sale with the lower cutoff levels at drugtestingcup.com
How to check drugs for fentanyl?
Take a bit of water and mix the drug compound you have with the water, once this is done use the Fentanyl testing strips to check for any traces of fentanyl.
The testing strips are highly adept at finding traces of specific drugs, with an accuracy rating of over 99%.
If you are looking for a way to protect yourself this is it.
DISCLAIMER
In no way do we condone the use of illegal drugs or substances. This short guide is here to help you save your life in the off chance that you do come across illegal drugs. We feel that it is important for everyone to have a tool which helps them stay safe. If you know of any illegal drugs being sold in your area, contact the local law enforcement.
For Forensic Use only
INTENDED USE
The FYL fentanyl drug test is a rapid visual immunoassay for the qualitative, presumptive detection on urine drug testing specimens at the cut-off concentrations listed below:
FYL (Fentanyl) 20 ng/ml
INTRODUCTION
Fentanyl is a synthetic opioid-related to phenylpiperidines. Fentanyl is approximately 100 times more potent than morphine. This agent is highly lipid-soluble and rapidly crosses the blood-brain barrier.
This is reflected in the half-life for equilibration between the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of approximately 5 minutes for fentanyl.
The levels in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid decline rapidly owing to redistribution of fentanyl from highly perfused tissue groups to other tissues, such as muscle and fat.
As saturation of less well-perfused tissue occurs, the duration of effect of fentanyl and sufentanil approaches the length of their elimination half-lives of between 3 and 4 hours. Fentanyl undergoes hepatic metabolism and renal excretion.
Therefore, with the use of higher doses or prolonged infusions, fentanyl becomes longer acting.
PRINCIPLE – background methods
The FYL fentanyl drug test (Urine) detects Fentanyl through visual interpretation of color development on the strip. Drug conjugates are immobilized on the test region of the membrane.
During testing, the specimen reacts with antibodies conjugated to colored particles and precoated on the sample pad.
The mixture then migrates through the membrane by capillary action, and interacts with reagents on the membrane. If there are insufficient drug molecules in the specimen, the antibody-colored particle conjugate will bind to the drug conjugates, forming a colored band at the test region of the membrane.
Therefore, a colored band appears in the test region when the urine is negative for the drug. If drug molecules are present in the urine above the cut-off concentration of the test, they compete with the immobilized drug conjugate on the test region for limited antibody binding sites.
This will prevent attachment of the antibody-colored particle conjugate to the test region. Therefore, the absence of a colored band at the test region indicates a positive result. The appearance of a colored band at the control region serves as a procedural control, indicating that the proper volume of specimen has been added and membrane wicking has occurred.
Fentanyl is a potent synthetic opioid that is used to manage severe pain. However, if someone takes too much fentanyl, it can lead to an overdose, which is a medical emergency.
Symptoms of a fentanyl overdose (fentanyl overdose symptômes) may include:
- Slow, shallow breathing or difficulty breathing
- Severe confusion or disorientation
- Pinpoint pupils (the black center of the eyes)
- Bluish or purple lips and nails
- Cold, clammy skin
- Extreme drowsiness or loss of consciousness
- Weakness or limpness
- Unresponsiveness to stimuli, such as being shaken or shouted at
If you suspect someone has overdosed on fentanyl, it’s important to call for emergency medical assistance immediately. Fentanyl overdoses can be life-threatening, and prompt medical attention can help prevent serious complications or even death.
The fentanyl crisis refers to the widespread use and abuse of fentanyl, a synthetic opioid that is many times more potent than heroin, morphine, or other traditional opioids. The crisis has been primarily driven by the illegal production and distribution of fentanyl, often mixed with other drugs like heroin, cocaine, or counterfeit pills.
The fentanyl crisis has led to a significant increase in overdose deaths across the globe, particularly in North America. According to the CDC, & World Health Organization (WHO), between 2010 and 2017, the number of opioid-related deaths in North America increased by 33%, with fentanyl and its analogs playing a major role in this increase.
The crisis has led to significant efforts by public health officials, law enforcement agencies, and healthcare providers to curb the availability and use of fentanyl. These efforts include increased access to addiction treatment and overdose reversal drugs like naloxone, increased public awareness campaigns, and stricter law enforcement measures targeting the illegal production and distribution of fentanyl.
However, the crisis remains a significant public health concern, and ongoing efforts will be required to address the root causes of the problem and prevent further harm to individuals and communities affected by fentanyl use and abuse.
| Weight | 0.01 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 3 × 2 × 1 in |
| Drug tested | FYL |
| Package size | Pack (25) |
Related products
Amphetamine Strips (25pack) (AMP Test Strips)
$0.65 per strip
Get Amphetamine Drug Test, convenient to use, our AMP drug test strips enable users to perform Amphetamine testing with complete ease and without seeking assistance.
- The AMP test strips provide quick results within five minutes.
- Our AMP testing strips possess a cutoff level of 1000 ng/ml.
Cocaine Drug Test Strips (25pack) (COC Drug Test Strips)
$0.65 per strip
| Cutoff level | |
| Cocaine | |
| 300 ng/ml | |
Alpha PVP (Flakka) Dip Stick
As Low As $0.95
Cutoff level: Flakka, APVP(α-PVP) 500 ng/ml
Fentanyl Test Strip 20ng/ml – Individual Pouch
As Low As $0.49
Cutoff level: Fentanyl 20 ng/ml
Oxycodone Drug Test Strips (OXY Drug Test)
$0.65 per strip
| Cutoff level | |
| Oxycodone | |
| 100 ng/ml | |
BUP drug test – Buprenorphine Drug test Strips (25pack)
$0.65 per strip
| Cutoff level | |
| Buprenorphine | |
| 10 ng/ml | |
Synthetic Marijuana Drug Test (25 pack) (K2 Drug Test Strips)
$0.65 per strip
| Forensic Use Only Cutoff level | |
| K2 | |
| 50 ng/ml | |
Clonazepam Test Strips (CLON test) 25 pack
$0.65 per strip
| Cutoff level | |
| Clonazepam | |
| 150 ng/ml | |
Ecstasy drug test – MDMA Drug Test Strip
$0.65 per strip
Cutoff level :
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine HCl 500 ng/ml
Xyl Test Strip – Xyl (XYL) Drug Test Strip
As Low As $0.69
| Cutoff level | |
| Xylazine | 1000 ng/ml |
Phencyclidine drug test – PCP drug test
$0.65 per strip
Get PCP drug test strips. convenient to use, our PCP (angel dust) test strips enable users to perform PCP urine testing with complete ease and without seeking assistance.
- The PCP urine test strips provide quick results within five minutes.
- Our PCP testing strips possess a cutoff level of 25 ng/ml.
THC Drug Test Strips – 50 ng – (Marijuana Test Strips)
$0.65 per strip
| Cutoff level | |
| 11-nor-Δ9-THC-9-COOH | |
| 50 ng/ml | |